
(Picture: Stanley Crooke, Ph.D. Founder and former CEO & Chairman)

(Picture: Eric Swayze, Ph.D. at Ionix Pharmaceuticals)
안녕하세요 보스턴 임박사입니다.
Ionix Pharmaceuticals는 Antisense Oligonucleotide 분야의 글로벌 선두기업이고 오래전에 블로그를 쓴 적이 있습니다.
BIOTECH (3) – Ionis Pharmaceuticals
최근에는 Neurology 분야에서도 좋은 결과가 많이 나오지만 NASH (Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis) 분야에도 3개의 약물이나 파이프라인에 있습니다. 이 중 AstraZeneca와 파트너쉽된 두개 약물과 자체 개발 약물인 ION224 (Ionix-DGAT2rx)가 있습니다.
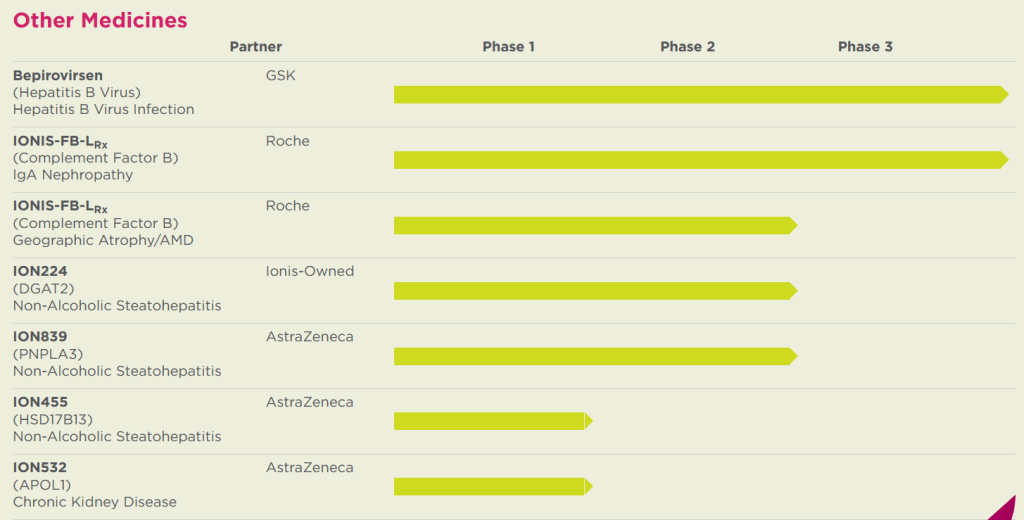
Ionis-AstraZeneca NASH drug deal은 2018년에 $30 Million upfront 및 총 $400 Million으로 계약을 했습니다.
AstraZeneca licenses Ionis’ clinical-phase antisense NASH drug – Fierce Biotech 4/9/2018
AstraZeneca has licensed a NASH candidate from Ionis. The Big Pharma is paying $30 million upfront to pick up the rights to the program and take it into the clinic.
Ionis advanced the asset through target validation and into development with the strategic support of AstraZeneca, which secured a front-row seat on its progress through a cardiovascular, metabolic and renal disease deal it struck in 2015.
The drug, like one previously licensed by AstraZeneca, features antisense technologies intended to improve affinity chemistry and cell-specific targeting.
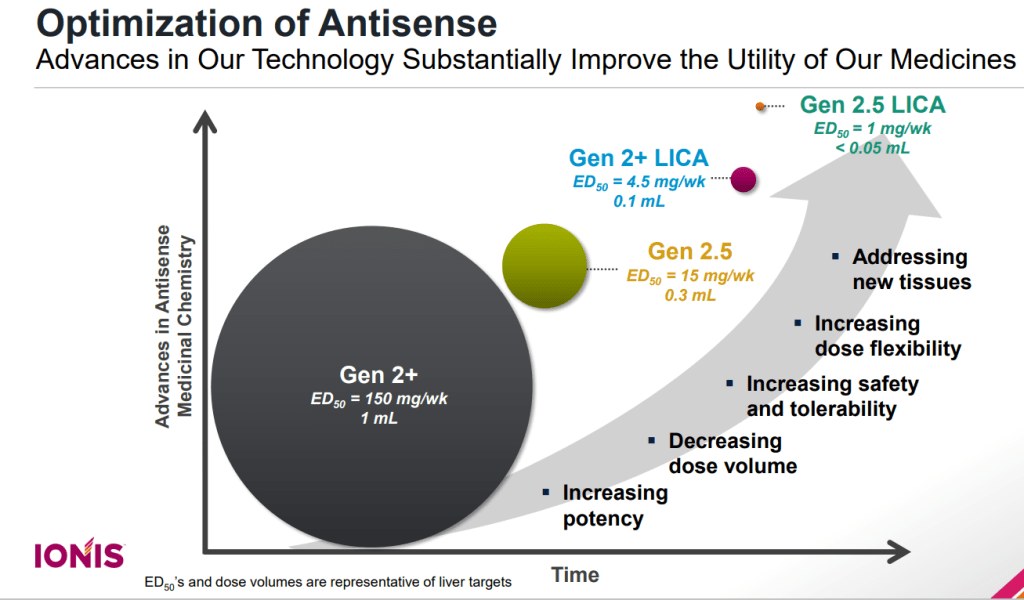
“This combination provides us with drugs that are substantially more potent than either Generation 2.5 or LICA alone, and supports administration of infrequent, very low doses, and even enables the potential for oral dosing,” Ionis COO Brett Monia said in a statement.
Gen 2.5 LICA는 현재 가장 약효와 독성 및 세포선택성 등에서 가장 앞선 기술 플랫폼입니다.
Beyond that, little is known publicly about the program. There are no online references to the drug, IONIS-AZ6-2.5-LRx, from before news of the licensing deal broke and neither Ionis nor AstraZeneca has disclosed its target.
Ionis has a long-standing interest in NASH, though. The biotech’s Akcea-partnered angiopoietin-like 3 protein drug AKCEA-ANGPTL3-LRx is currently undergoing phase 2 testing in patients with NASH and other conditions to assess its effect on endpoints including liver fat. A phase 2 trial of another Ionis drug, IONIS-DGAT2Rx, is also using liver fat as an endpoint. The IONIS-DGAT2Rx trial is enrolling type 2 diabetics at risk of NASH.
By offloading its latest NASH drug, Ionis has landed a $30 million upfront fee and a chance to pull in up to $300 million in milestones. If IONIS-AZ6-2.5-LRx comes to market, AstraZeneca will pay Ionis tiered royalties that top out in the low teens.
The financial terms are the same as for the last Ionis drug licensed by AstraZeneca. That deal gave AstraZeneca the rights to the kidney disease candidate IONIS-AZ5-2.5Rx, now known as AZD2373.
2020년에 UC San Diego School of Medicine의 Rohit Roomba 교수 연구진에서 ION224 (Ionix-DGAT2rx)의 13주 임상2상 결과를 The Lancet Gastroenterology and Hepatoloty에 발표했습니다.
Novel Antisense Drug Shows Promise in Slowing Fatty Liver Disease – UC San Diego Health 6/16/2020
Using a first-of-its-class drug in a clinical trial, an international research effort headed by a scientist at University of California San Diego School of Medicine reports that inhibition of a key enzyme safely and effectively improved the health of persons with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a chronic metabolic disorder that affects hundreds of millions of people worldwide.
The gene silencing approach represents a novel way to reverse NAFLD. The findings are published in the June 15, 2020 online issue of The Lancet Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
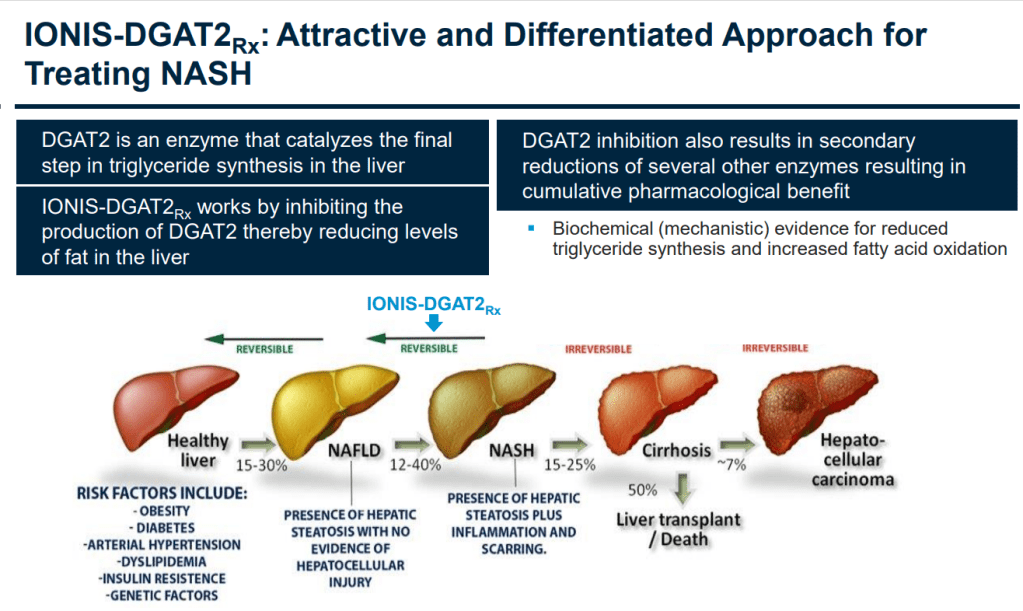
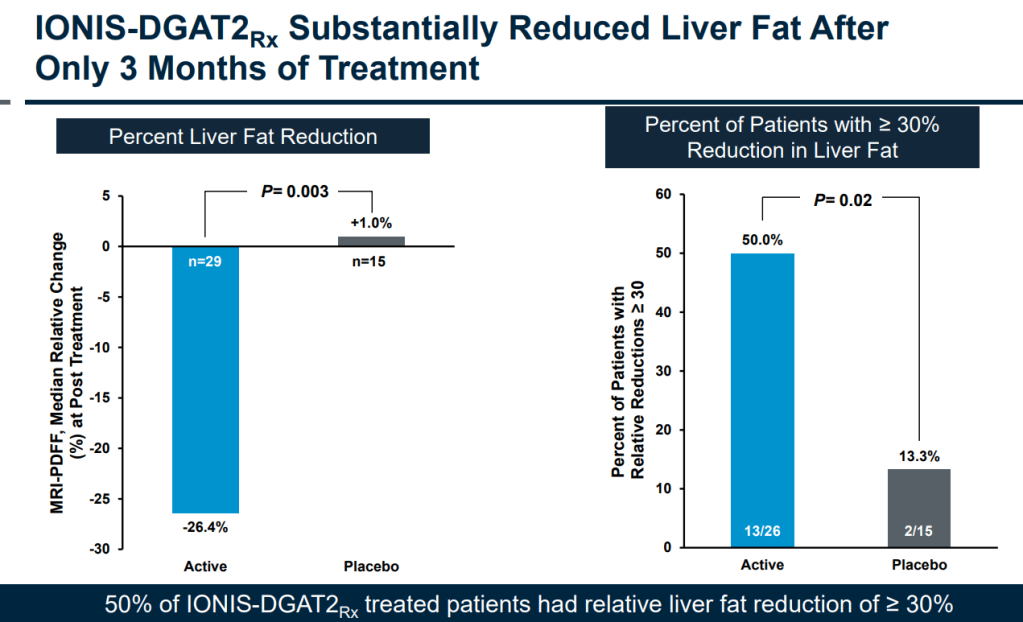
아래는 2018년 Investor Day에서 발표한 자료 중 발췌한 것입니다. ION224는 NASH에서 이전 단계인 NAFLD 단계로 개선할 수 있는 약물입니다.
44명의 Hepatic Steatosis with Type 2 Diabetes 환자에게 13주간 매주 SC 주사를 한 이후에 약물을 중단하고 13주의 기간의 경과를 보는 임상2상의 초기 결과를 보고했습니다.
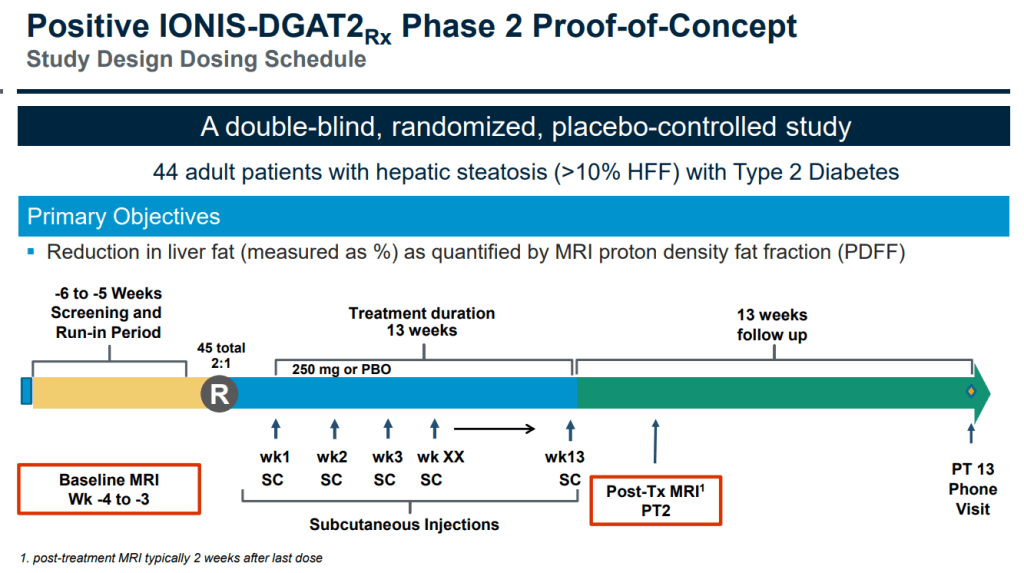
3개월 치료 후 50% 환자에서 < 30% 이상의 간지방 감소를 보였습니다.
NAFLD occurs when fat accumulates in liver cells due to causes other than excessive alcohol intake. The precise cause is not known, but diet and genetics are believed to play substantial roles. The condition is typically not noticed until the disease is well-advanced, and perhaps has transitioned to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a progressive form that can lead to cirrhosis, liver cancer and liver failure.
There is no cure. Treatment primarily consists of ameliorating contributory factors, such as losing weight, improving diet, exercising more and controlling for other conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension. No Food and Drug Administration-approved medications exist. In worst cases, a liver transplant may be required.
“NAFLD wasn’t even recognized as a disease three decades ago; now it is alarmingly prevalent, affecting roughly one-quarter of all Americans and emerging as one of the leading causes for liver transplant in the United States,” said the study’s lead author Rohit Loomba, MD, professor of medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology at UC San Diego School of Medicine and director of the UC San Diego NAFLD Research Center. “Given its relative ubiquity and its potentially calamitous consequences, safe and effective treatments are absolutely needed.”
In the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled Phase II trial, Loomba and colleagues enrolled 44 qualifying participants at 16 sites in Canada, Poland and Hungary. For 13 weeks, participants were injected with either an antisense inhibitor called IONIS-DGAT2 or a placebo. The inhibitor, produced by Carlsbad-based Ionis Pharmaceuticals, interferes with Diacylglycerol-O-acyltransferace or DGAT2, one of two enzyme forms required to catalyze or accelerate the production of triglycerides, a type of fat found in blood. High levels of triglycerides boost fat storage throughout the body, including the liver.
The researchers found that after 13 weeks of treatment, participants who received the enzyme inhibitor experienced measurable reductions in fatty liver levels compared to baseline, without elevated levels of fats, enzymes or sugars in the blood. There were six reported serious adverse events, including a cardiac arrest and deep vein thrombosis, but the researchers determined the events were unrelated to the study drug.
“These findings showed robust reduction in liver fat by MRI without corresponding increases in blood lipids,” said Loomba. “Given significant proportion of patients achieving roughly a 30 percent reduction in MRI-PDFF, the threshold that corresponds with higher odds of histologic response when treated for a longer duration, it looks like after just 13 weeks of treatment, the drug was actually slowing progression of NAFLD to NASH.
“All of this is very encouraging and argues for the next step: longer term trials to further investigate the potential of this drug in improvement of liver histologic features associated with NASH, the progressive sub-type of NAFLD.”
Co-authors of the study include: Erin Morgan, Lynnetta Watts, Shuting Xia, Lisa A. Hannan, Richard S. Geary, Brenda F. Baker and Sanjay Bhanot, all at Ionis Pharmaceutical, Carlsbad, Calif.
Funding for this research came from Ionis Pharmaceuticals. Loomba is supported, in part, by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (grants R01DK106419 and P30DK120515).
Disclosures: Rohit Loomba is a consultant or advisory board member for Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Bird Rock Bio, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myer Squibb, Celgene, Cirius, CohBar, Conatus, Eli Lilly, Galmed, Gemphire, Gilead, Glympse bio, GNI, GRI Bio, Intercept, Ionis, Janssen Inc., Merck, Metacrine, Inc., NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Prometheus, Sanofi, Siemens, and Viking Therapeutics. In addition, his institution has received grant support from Allergan, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cirius, Eli Lilly and Company, Galectin Therapeutics, Galmed Pharmaceuticals, GE, Genfit, Gilead, Intercept, Grail, Janssen, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Merck, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, NuSirt, Pfizer, pH Pharma, Prometheus, and Siemens. He is also co-founder of Liponexus, Inc. His co-authors are all employees and/or stockholders of Ionis Pharmaceuticals.
최근에 160명 환자에 대한 51주 경과에 대한 임상2상 발표를 했는데 120 mg을 맞은 환자에서 44%가 >50% 의 Liver Steatosis 개선을 보였습니다. 아주 긍정적입니다. 그리고 32%는 1기 이상의 Stage 개선을 보였습니다. 이러한 임상결과를 가지고 Pivotal clinical trials로 진입할지 기대됩니다.
Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Nasdaq: IONS) announced positive results from a Phase 2 study of ION224, an investigational DGAT2 antisense inhibitor in development for the treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), previously referred to as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). The study met its primary endpoint at both doses (120 mg and 90 mg), achieving liver histologic improvement, and also met the important secondary endpoint of MASH resolution.
Key highlights from the 160-patient study at 51 weeks included:
- ION224 achieved statistically significant liver histologic improvement as measured by at least a 2-point reduction in NAFLD Activity Score (NAS)* (p<0.001 (120 mg) and p=0.015 (90 mg)).
- Subgroup analysis indicated that significant improvements in the primary endpoint were observed in patients with both F2 and F3 (advanced) fibrosis.
- ION224 achieved statistically significant MASH resolution without worsening of fibrosis, as measured by biopsy (p=0.039).
- 44% of patients treated with 120 mg achieved ≥50% relative reduction in liver steatosis as measured by MRI-PDFF compared to 3% for placebo.
- 32% of patients treated with 120 mg achieved a ≥1 stage improvement in fibrosis without worsening steatohepatitis as measured by biopsy compared to 12.5% for placebo.
- ION224 was safe and well-tolerated in the study.
“This Phase 2 trial of ION224 is the first to demonstrate clinical evidence that the reduction of hepatic fat after DGAT2 inhibition correlates with improvements in MASH histological endpoints,” said Rohit Loomba, MD, MHSc, professor of medicine and chief, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of California San Diego; founding director, MASLD Research Center, University of California San Diego. “I believe ION224 offers a unique precision medicine opportunity with an approach that is potentially complementary to others in development for MASH, and I look forward to continued evaluation of this important investigational medicine.”
MASH is the more severe form of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and can lead to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and liver-related death. ION224 is an investigational LIgand-Conjugated Antisense (LICA) medicine designed to reduce the production of diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2 (DGAT2) to treat patients with MASH.
“Reducing the production of DGAT2 enzyme decreases the overproduction of triglycerides that contribute to excess liver fat, which can result in liver damage and inflammation. We are encouraged by these ION224 data, showing that a monthly subcutaneous medicine targeting DGAT2 has the potential to improve MASH and prevent its progression to more severe stages, including advanced liver fibrosis and cirrhosis,” said Sanjay Bhanot, MD, PhD, senior vice president and chief medical officer at Ionis. “The inhibition of DGAT2 represents a novel approach for MASH, a progressive disease in need of better treatment options. We look forward to sharing the full results from this study at an upcoming medical conference and discussing next steps to advance this potentially promising therapy for patients.”
In this study, ION224 was safe and well-tolerated in MASH participants. Those in the ION224 study arms did not experience any worsening of hepatic or renal function or gastrointestinal side effects, and there was a lower rate of early termination compared to placebo. Additionally, there were no on-study deaths or treatment-related serious adverse events.
The adaptive Phase 2, two-part, multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was designed to assess the efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics of multiple doses of ION224 when administered subcutaneously once-monthly in adults with MASH. The study enrolled 160 patients to receive ION224 or placebo over a period of 49 weeks. In Part 1, 93 patients were randomized 1:1:1 to the three dose cohorts (60, 90, and 120 mg) and within each dose cohort, randomized 3:1 to receive ION224 or placebo. In Part 2, an additional 67 patients were randomized 1:1 to two selected dose cohorts (90 and 120 mg) and then in a 2:1 ratio to receive either ION224 or placebo within each cohort. The study was powered for the primary endpoint, which was the percentage of patients who achieved MASH histologic improvement, defined as achieving at least a 2-point reduction in NAS with at least 1-point improvement in hepatocellular ballooning or lobular inflammation, and without worsening of fibrosis at end of the treatment period.
About ION224
ION224 is an investigational LIgand-Conjugated Antisense (LICA) medicine designed to reduce the production of diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2 (DGAT2) to treat patients with MASH. DGAT2 is an enzyme that catalyzes the final step in triglyceride synthesis in the liver. Reducing the production of DGAT2 should therefore decrease triglyceride synthesis in the liver. Additionally, there is evidence of an increase in both fatty acid oxidation and oxidative gene expression associated with antisense inhibition of DGAT2. ION224 offers a unique approach, which is potentially complementary to other therapies currently in clinical development.
About Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH)
MASH is the more severe form of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MASLD). It is related to the epidemic of obesity, pre-diabetes and diabetes. Unlike liver disease caused by alcohol consumption, MASH is the result of an accumulation of fat in the liver, which can lead to inflammation and cirrhosis, an advanced scarring of the liver that prevents the liver from functioning normally. About 20% of MASH patients are reported to develop cirrhosis, which is associated with increased risk of liver-related and overall mortality.i MASH is the fastest growing indication for liver transplantation in the U.S. and Europe.ii
In 2023, several multinational liver societies made the recommendation to update NAFLD to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and to update non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). Ionis has adopted the use of MASH to describe this Phase 2 trial. ION224-CS2 is registered on clinicaltrials.gov as a study in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and was registered before the recommended update.
About Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
For three decades, Ionis has invented medicines that bring better futures to people with serious diseases. Ionis currently has five marketed medicines and a leading pipeline in neurology, cardiology, and other areas of high patient need. As the pioneer in RNA-targeted medicines, Ionis continues to drive innovation in RNA therapies in addition to advancing new approaches in gene editing. A deep understanding of disease biology and industry-leading technology propels our work, coupled with a passion and urgency to deliver life-changing advances for patients. To learn more about Ionis, visit Ionispharma.com and follow us on X (Twitter) and LinkedIn.
Forward-looking Statements
This press release includes forward-looking statements regarding Ionis’ business and the therapeutic and commercial potential of ION224, additional medicines and technologies. Any statement describing Ionis’ goals, expectations, financial or other projections, intentions, or beliefs is a forward-looking statement and should be considered an at-risk statement. Such statements are subject to certain risks and uncertainties, including but not limited to those related to our commercial products and the medicines in our pipeline, and particularly those inherent in the process of discovering, developing and commercializing medicines that are safe and effective for use as human therapeutics, and in the endeavor of building a business around such medicines. Ionis’ forward-looking statements also involve assumptions that, if they never materialize or prove correct, could cause its results to differ materially from those expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. Although Ionis’ forward-looking statements reflect the good faith judgment of its management, these statements are based only on facts and factors currently known by Ionis. Except as required by law, we undertake no obligation to update any forward-looking statements for any reason. As a result, you are cautioned not to rely on these forward-looking statements. These and other risks concerning Ionis’ programs are described in additional detail in Ionis’ annual report on Form 10-K for the year ended Dec. 31, 2023, which is on file with the SEC. Copies of this and other documents are available at www.ionispharma.com.
Ionis Pharmaceuticals® is a registered trademark of Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
* Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Activity Score (NAS) with at least 1-point improvement in hepatocellular ballooning or lobular inflammation, and without worsening in fibrosis stage.
iLe MH, et al. Clin Mol Hepatology 2022;28:841–850.
iiEstes C, et al. Hepatology. 2018;67(1):123-133.
